Cloud migration is moving your digital operations to the cloud to boost efficiency and reduce costs. This guide covers the strategies, benefits, and tools you need to know.
Key Takeaways
- Cloud migration enhances business operations by providing cost efficiency, scalability, improved performance, and robust security measures.
- Successful migration strategies, such as rehosting, replatforming, and refactoring, are essential for optimizing resources and achieving desired outcomes.
- Effective preparation, planning, and execution of the migration process, alongside the right choice of tools and cloud providers, can mitigate common challenges and ensure a smooth transition.
Understanding Cloud Migration
The transition of digital operations into cloud environments is a pivotal maneuver that underpins the modernization of business functions. The drive towards adopting cloud services stems from the desire to harness enhanced features provided by these platforms, including but not limited to, higher uptime, swifter access to data resources, and more agile update deployment capabilities—cornerstones for actualizing a comprehensive transformation into a cloud-centric enterprise with an eye on longevity.
Undeniably crucial in its role within organizational strategy development is migrating workloads to the cloud. This move unlocks invaluable advantages such as financial savings and nimble adaptability. These attributes are essential tools for organizations looking to carve out their niche amid competitive markets through heightened efficiency in operational procedures while accommodating fluctuating consumer needs and evolving economic landscapes swiftly.
Nonetheless, it’s imperative that meticulous oversight governs the entire migration process so that risks can be properly navigated away from critical paths—ensuring continuous adherence to security protocols and regulatory compliance standards during each step toward total integration with chosen cloud infrastructures.
Core Benefits of Cloud Migration
Transitioning to cloud computing can revolutionize the way a company functions, presenting significant advantages such as considerable cost reductions, improved scalability and adaptability, better performance levels, and strong security protocols. Companies that integrate cloud-based solutions into their operations typically discover they are more agile in adapting to market fluctuations and expediting innovation.
Exploring these foundational benefits Reveals the integral role they play in facilitating successful cloud adoption for organizations.
Cost Savings
Shifting to a cloud environment can lead to significant financial benefits, particularly in terms of cost savings. Organizations that transition away from traditional data centers to cloud platforms could see reductions in IT operational costs by as much as 50%. This is largely because the overheads associated with physical resources, ongoing maintenance, and property expenses are greatly diminished within a cloud setup. Instead of heavy upfront capital investments for infrastructure, companies using the cloud enjoy an operating expense model which allows them to pay on-the-go for technological services utilized – enhancing both cash flow management and financial nimbleness.
Each variety of cloud platforms brings forth different pricing structures designed to assist organizations in effective budget management. For instance, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions might be offered on a per-user basis while Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) models usually operate based upon the actual consumption of resources.
Organizations may achieve anywhere between 10% and 30% savings after strategically migrating workloads into the cloud—this range being influenced by their unique demands and approaches toward migration. When enterprises commit to purging superfluous applications and refining how they allocate resources within these environments. They’re likely to realize even greater economies regarding their investment into moving towards modernized computing frameworks.
Scalability and Flexibility
The transition to cloud computing facilitates the expansion of business operations with remarkable flexibility and convenience. Within these cloud environments, organizations can modify their resource utilization in real-time, allowing for quick adaptation to market fluctuations and consumer demands. Such scalability is invaluable for companies that encounter variable workloads as it mitigates the necessity for excessive provisioning while also decreasing expenses linked to underutilized resources.
Hybrid clouds offer a strategic approach by distributing workloads between on-premises infrastructure and cloud-based services, which enhances operational efficiency through an integrated system. Retailers are among those increasingly incorporating such solutions into their strategies in order to boost efficiency and elevate customer experiences.
By tapping into the advantages of cloud capabilities, enterprises can expedite software service deployment processes, customize them more fittingly towards particular requirements, thus ensuring successful integration with broader cloud computing frameworks.
Enhanced Performance
Migrating to cloud environments often results in heightened performance, a key advantage for modern businesses. Applications that are cloud native inherently exhibit superior reliability and lower downtime compared to their traditional counterparts, an essential factor for the smooth execution of business operations and securing a satisfactory customer experience. Service providers of the cloud play an integral role by consistently delivering updates which sustain ideal functionality and bolster security measures.
Cloud services Elevate application performance by reducing latency via widespread resource distribution across the globe. The efficient allocation of hardware resources within these cloud environments stimulates innovation in software development while boosting overall efficiency in operation management. This enhanced capacity empowers enterprises to provide more effective cloud infrastructure services, ensuring they maintain a competitive edge within their respective markets.
Improved Security
Enhanced security is a primary advantage of migrating to the cloud. Opting for services from public cloud providers can offer superior security features that surpass the capabilities often achievable by individual businesses. These providers incorporate automatic updates, sophisticated tools for security management, and foundational platform-level protections designed to safeguard applications and data against various threats. Implementing these stringent security protocols helps preserve both the integrity and privacy of business data.
It’s imperative in migration processes to adhere strictly to best practices in terms of secure governance. This involves strengthening data protection as well as improving measures related to compliance and governance in order to reduce potential risks associated with regulatory infractions or breaches of sensitive information.
Not only do such robust measures instituted by cloud service vendors fortify defense mechanisms, but they also facilitate reductions in expenses related directly to maintaining an expansive on-site security framework. The high-grade safety infrastructure provided through these services aids companies not just securely but also cost-effectively scale their operations into the cloud environment.
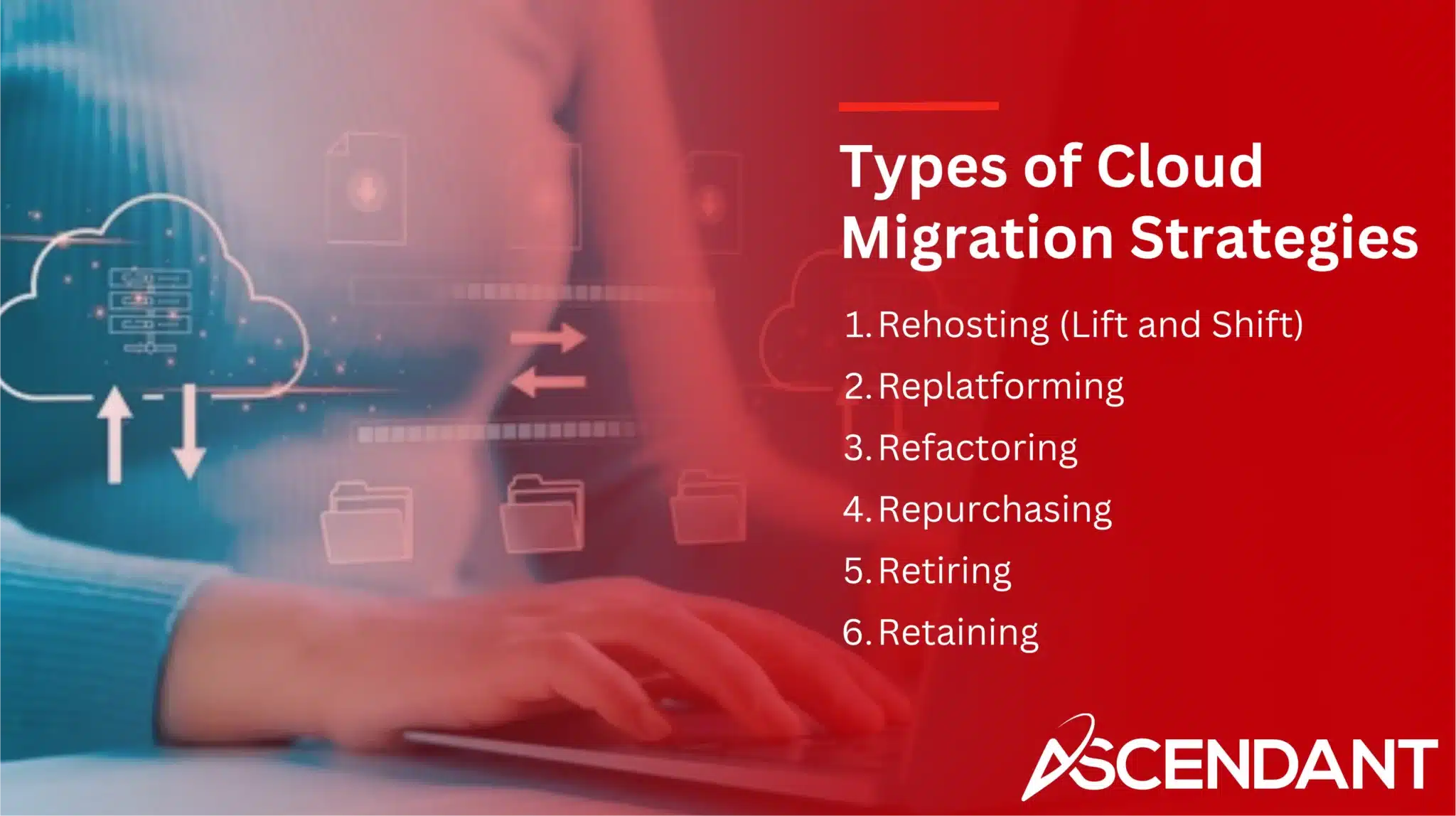
Types of Cloud Migration Strategies
It is essential to select an appropriate cloud migration strategy for a successful shift. The ‘six R’s of migration’ comprise the recognized approaches: Rehosting, Replatforming, Refactoring, Repurchasing, Retiring and Retaining. Tailored to various business requirements and IT infrastructure setups, each of these strategies provides distinct benefits. Integrating both public and private cloud solutions often leads to enhanced operations through a hybrid approach.
To ensure that organizations can execute their migrations with maximum efficiency while adhering closely to their overarching business objectives, it is vital to grasp the nuances of each method within these migration strategies in depth. Understanding how they apply specifically and what advantages they confer will aid this process significantly.
Rehosting (Lift and Shift)
Transferring an application to the cloud using minimal changes, a process referred to as “lift and shift,” is essentially rehosting its components. This strategy is typically the fastest route for migration, facilitating organizations in attaining swift gains on their investments. As an example, a database might be initially relocated to a virtual machine hosted in the cloud before being transitioned to a managed database service for enhanced administration.
Nevertheless, not every legacy application may be appropriate for rehosting since it doesn’t fully exploit the advantages of cloud-native capabilities and could impede optimization efforts. Even so, due to its efficiency in enabling businesses to expedite their move into the cloud with prospects of advancing optimizations later on, rehosting continues to be a favored option among organizations.
Replatforming
Replatforming involves making minor adjustments to optimize applications for the cloud while keeping the core architecture intact. This approach allows businesses to take advantage of cloud-specific features and customization without a complete overhaul of their applications. For example, migrating to an autonomous cloud database service that updates automatically can significantly enhance performance and reduce maintenance efforts.
By replatforming, organizations can achieve a balance between cost, time, and performance, making it an attractive option for many businesses. It enables a smoother transition to the cloud while setting the stage for future enhancements and scalability.
Refactoring
The process of refactoring, or fundamentally reworking, the application’s architecture, is undertaken to fully utilize cloud-native capabilities. Opting for this approach often aligns with objectives such as incorporating new functionalities, enhancing system performance, or achieving more effective scalability within applications.
Despite its demanding nature in terms of time and resources spent, refactoring can lead to the creation of applications that are exceptionally optimized for the cloud environment. Such applications tend to be scalable and robust – qualities that make them particularly compatible with cloud-native features.
Repurchasing
Repurchasing involves moving to a different application designed for the cloud, typically by switching to a Software as a Service (SaaS) model. This approach is appropriate for companies seeking advanced software options that more closely match their business requirements. It enables them to take advantage of modern cloud innovations without being limited by current applications they have in place.
Retiring
During the cloud migration process, retiring outdated applications that have become obsolete is a key step. By pinpointing and eliminating these unnecessary programs, IT operations can be simplified, maintenance expenses reduced, and overall performance improved within the new cloud environment. This aspect of the migration process ensures a more streamlined and effective shift to the cloud setup.
Retaining
Retaining involves postponing the transfer of specific applications until there is a strong justification for their migration. This decision may be made by organizations because the applications have been recently updated or because the motives for migrating them are not well-defined.
It is essential to conduct regular evaluations of these applications that are being retained in order to decide whether they ought to be migrated at a later time.
The Cloud Migration Process
The journey to the cloud typically involves five distinct stages.
- Preparation
- Planning
- Execution of migration
- Operation post-migration
- Ongoing optimization
Every stage is instrumental in facilitating a seamless switch and maximizing the benefits associated with moving to the cloud environment, such as agility and cost savings among others. A well-crafted migration strategy for the cloud must outline an in-depth approach that ensures digital assets are moved efficiently while disruption is kept at bay.
In absence of a meticulously formulated strategy for migration, organizations might confront substantial obstacles impeding successful adoption of cloud services. It’s crucial that comprehensive planning permeates all levels of an organization during extensive migrations, navigating through intricacies inherent within current IT frameworks to sidestep common setbacks commonly encountered during this process.
Assessing Current Infrastructure
The initial phase of the cloud migration process necessitates a thorough assessment of an organization’s current IT setup. This entails scrutinizing existing systems to determine whether they should be kept as-is, redeveloped, or completely replaced. Such evaluations are instrumental in understanding what resources are at hand while pinpointing any skill shortages or technological deficiencies that could potentially hinder the migration effort. Engaging with consulting firms can aid organizations in achieving a seamless transition by offering specialized knowledge and strategies designed to meet their specific needs.
Conducting a detailed examination of present applications and infrastructure is pivotal for businesses poised to migrate to the cloud. During this stage, an exhaustive review is conducted which encompasses everything from on-premises data centers and physical servers to those workloads deemed critical for business operations, ensuring companies have laid proper groundwork before undertaking such a significant technological shift.
Defining a Cloud Migration Strategy
Formulating a comprehensive cloud migration strategy is crucial for ensuring a seamless transition and maintaining operational effectiveness. This approach should encompass specific objectives, meticulously crafted business justifications for relocating each workload, as well as insights into the prospective cloud setting. The role of third-party contributors and the order in which workloads will be transferred also merit consideration within this plan.
An effective migration agenda must address budget projections, procedures to clean or secure data through encryption methods, along with any adaptations required for applications. Employing tools like cloud cost calculators can assist in projecting future expenses under practical assumptions to support a thoroughly informed migration approach. Constructing detailed business cases assists organizations by clarifying anticipated total costs of ownership (TCO) within the new cloud milieu relative to existing TCO metrics.
Planning and Preparation
To guarantee a successful cloud migration, thorough planning and careful preparation must be undertaken. This critical stage includes safeguarding important data through backups and performing compliance verifications to adhere to legal and regulatory standards. Such meticulous preparation is pivotal in reducing risks and facilitating an effortless shift into the cloud environment.
Executing the Migration
The implementation of the migration is a crucial stage where it’s essential to keep downtime to an absolute minimum in order to maintain continuous business operations. Ensuring that systems are set up for high availability during this period can bolster resilience and ward off interruptions in service. Utilization of adept monitoring solutions grants instantaneous insights into the progress of migrations, enabling quick identification and rectification of any performance bottlenecks.
Tools designed specifically for cloud migrations facilitate automation and simplify the process of moving data, which helps maintain its integrity while minimizing possible disturbances. Technologies such as SnapMirror contribute significantly towards smooth cloud transitions by providing ease in either migrating data to or from cloud environments, thereby promoting an effective and seamless changeover.
Post-Migration Optimization
Optimization following migration is key to fully capitalizing on the advantages of moving to a cloud environment. Tools for validating performance are critical as they assist in evaluating and affirming the effectiveness of the migration process. Real-time analytics and tracking functionalities provided by monitoring tools play an important role in sustaining operational efficiency and performance post-migration.
Ongoing improvements, guided by feedback and data on performance, guarantee that an organization can make the most out of its new cloud environment’s benefits.
Common Challenges in Cloud Migration
Despite the numerous benefits, cloud migration comes with its own set of common cloud migration challenges. These include cost management, data security, compliance, skill gaps, and issues with legacy systems. Managing these challenges effectively is crucial for a successful migration. Organizations must address governance and compliance policies to ensure data security during the migration process.
Understanding new fee structures, billing cycles, and resource consumption can be complex, often leading to unexpected costs. Additionally, overprovisioning resources during the migration process can result in initial overspending.
Identifying and addressing gaps in skills or technologies is also essential to ensure cloud readiness and avoid disruptions.
Legacy Applications
During the migration process, legacy applications frequently encounter compatibility challenges and may need to be restructured. It is essential to evaluate these applications for their readiness for the cloud and identify required changes as part of an effective migration strategy. Making informed decisions about which legacy applications should be preserved or reconstructed can profoundly influence the entire migration endeavor.
For example, healthcare providers are transitioning from mainframe systems to cloud-based services in order to enhance data handling and adhere to regulatory requirements. This illustrates how conventional systems stand to gain from undergoing modernization.
Data Security and Compliance
During the transition to cloud services, maintaining data security and adhering to compliance regulations is paramount, necessitating stringent safeguards. It’s critical that the migration strategy explicitly incorporates and addresses these safety and regulatory demands, including adherence to legal frameworks like HIPAA for healthcare information privacy and GDPR for data protection in Europe.
Cloud providers deliver various features aimed at bolstering security without imposing extra burdens on businesses. These offerings typically include automatic updates related to security as well as advanced tools specifically designed for this purpose. By integrating such inherent protections, cloud vendors play a crucial role in helping organizations secure their assets while conforming to prevalent industry regulations.
Managing Costs
If not carefully evaluated and planned for, cloud migration may lead to unanticipated hikes in expenses. It is vital to practice effective cost management so that organizations can fully capitalize on their investment while steering clear of unforeseen costs. Through comprehensive budgeting and strategic planning, companies can control their expenditures associated with the cloud and reduce the risks tied to unexpected financial outlays.
Healthcare providers exemplify entities for whom migrating to the cloud has streamlined IT operations, curtailed expenses, and met data retention standards. By adopting robust cost management strategies, these organizations are able to reap considerable financial benefits and enhance their fiscal health overall.
Skill Gaps
When organizations transition to cloud environments, they frequently encounter skill shortages. To ensure a successful migration to the cloud, it’s imperative that employees develop competencies aligned with cloud-related technologies. Teams currently in place might lack the necessary skills for proficient management of these environments, which underscores the importance of mitigating this disparity by providing specific training opportunities.
As cloud resources and technologies continue to advance, maintaining an ongoing commitment to learning and improving one’s capabilities in this area becomes indispensable for effective resource management. Enhancing their expertise in cloud services enables staff members not only to heighten operational efficiency but also guarantees a smooth integration of these solutions into organizational processes.
Choosing the Right Cloud Provider
Choosing an appropriate cloud provider is a pivotal choice that greatly affects the outcome of your move to the cloud. This decision requires careful consideration of your company’s distinct needs, the array of services on offer, and financial limitations. It’s vital to comprehend the future plans and potential growth offered by a provider’s service roadmap in order to judge how well it fits with your prospective requirements.
In advance of settling on a cloud provider, it is imperative to thoroughly scrutinize their portfolio for aspects such as variety of services provided, system performance levels, pricing models, and customer assistance options. Conducting an exhaustive comparison between various cloud providers guarantees that you select one capable of addressing specific business demands while facilitating successful migration objectives.
Evaluating Cloud Providers
It is essential to assess cloud providers thoroughly to confirm that they align with the specific needs of your business and facilitate your migration objectives. When doing so, it’s important to evaluate various elements such as the breadth of services offered, system performance, cost structures, and available support options. For instance, one leading cloud provider delivers an expansive array of over 250 distinct services. Competitors like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud also provide a wide range of powerful capabilities in their service offerings, each bringing unique strengths within their public clouds.
For businesses aiming for strategic alignment and fulfillment of operational demands through cloud adoption, a comprehensive comparison between potential cloud providers is paramount. Scrutinizing these key components assists organizations in making choices that not only satisfy immediate requirements but also resonate with long-term strategies and goals.
Comparing Cloud Services
When comparing cloud services, key factors to assess include certifications, data security, service reliability, and migration support. Geographic availability is also crucial as it can significantly affect performance and compliance. Each cloud provider has unique strengths; for instance, AWS has the most comprehensive range of services, Azure excels in artificial intelligence and machine learning, and Google Cloud is strong in supporting containerized workloads.
Organizations should consider these factors and the specialized services offered by each provider to make an informed decision. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud helps businesses choose the provider that best meets their specific needs.
Essential Cloud Migration Tools
The migration process to the cloud is significantly enhanced by specialized cloud migration tools. With functionalities such as data replication, performance monitoring, and pre-migration assessment at their disposal, these tools facilitate a seamless and effective transition. They assist organizations in automating procedures while maintaining data integrity, which aids in reducing any possible interruptions during the course of migration.
We should examine some key cloud migration tools that are instrumental across various stages of the migration process.
Migration Assessment Tools
Assessment tools for migration are critical in gauging preparedness and strategizing the process of transitioning to the cloud. By scrutinizing current IT setups, these instruments pinpoint applications suitable for transfer while illuminating potential hazards. Foreseeing incompatible software and requisite alterations prior to initiating the migration can curb risks and foster a more seamless shift.
Incorporating such assessment utilities cultivates an alignment with overarching business goals as well as enhancing the efficacy of the cloud migration strategy. These tools offer crucial intelligence that aids enterprises in formulating a more proficient plan for their journey to the cloud, helping them circumvent typical obstacles often encountered during this complex process.
Data Transfer Tools
Ensuring secure and effective data migration hinges on the use of reliable data transfer tools. Cloud providers offer robust one-click backup recovery solutions that protect data throughout its migration, providing peace of mind by allowing for restoration to its original state if complications arise. Features designed for data replication facilitate precise and protected duplication of information, preserving its integrity while in transit.
It is critical to preserve both the integrity and confidentiality of information during cloud migration through secure data transfers. Leveraging appropriate backup and replication instruments can markedly improve both the safety and efficacy with which data is migrated into the cloud environment.
Monitoring and Management Tools
Tools for monitoring and management play a critical role in the successful management of cloud resources after migrating. They offer organizations the ability to ensure peak performance and efficient use of resources by delivering analytics and tracking functions in real time.
As an illustration, Cloud Sync from NetApp aids with migrations from systems that are not based on ONTAP, improving abilities to manage clouds.
Successful Cloud Migration Case Studies
Case studies on cloud migration from the real world offer essential insights and lessons that are beneficial for guiding subsequent migrations. These examples showcase effective strategies and best practices which can be adapted across different industry sectors.
Retail Industry
Struggling to maintain their online presence due to the extensive video and image storage needs, a worldwide apparel seller found solace in cloud technology. This strategic move boosted both customer satisfaction and streamlined their operations. The shift to cloud computing offered scalable solutions for storage that catered adeptly to the retailer’s challenges by facilitating unbroken online functionality.
The adoption of cloud technology markedly enhanced how customers interact with product information and rich media content, showcasing swift access improvements. This instance exemplifies the revolutionary impact that migrating to the cloud can have within retail sectors, underscoring its transformative capabilities for businesses facing similar digital infrastructure demands.
Healthcare Sector
Monash University undertook a migration process to the cloud with the aim of improving data management and compliance. They faced considerable obstacles, particularly in ensuring that student services, business functions, and research activities remained uninterrupted throughout their move to the cloud. With meticulous planning and careful implementation, they achieved a seamless transition without impeding these operations.
This instance of successful cloud adoption at Monash University underscores improved outcomes in data handling and adherence to regulations post-migration. It serves as an exemplar within the healthcare field for how strategic foresight and diligent execution are critical components when facilitating a smooth transition into cloud computing environments.
Financial Services
The case of Capital One exemplifies the significant impact that cloud technology can have on reshaping business operations in the finance sector. The company’s move to the cloud resulted in notable cost savings and a boost in operational efficiency, allowing for faster delivery of services and refinement of their business practices.
In its strategic overhaul, Capital One harnessed the process of migrating to the cloud as a means to revamp its IT infrastructure. This shift brought about marked enhancements in system performance and nimbleness, illustrating how adopting cloud technology can be crucial for stimulating expansion and fostering innovation within financial enterprises.
 Summary
Summary
Cloud migration is a powerful enabler for businesses looking to modernize their operations, achieve cost savings, and enhance performance and security. By understanding the different cloud migration strategies and carefully planning the migration process, organizations can navigate challenges and maximize the benefits of moving to the cloud. The use of specialized migration tools and selecting the right cloud provider further contribute to a successful migration journey.
As demonstrated by real-world case studies, cloud migration can lead to significant improvements in operational efficiency, customer experience, and compliance. By embracing cloud technology, businesses can position themselves for future growth and innovation. The journey to the cloud is not without its challenges, but with the right strategies and tools, it can be a transformative experience that drives long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main phases of the cloud migration process?
The main phases of the cloud migration process are preparation, planning, migration, operation, and optimization. Each phase is crucial for ensuring a smooth transition to the cloud.
How does cloud migration result in cost savings?
Moving to the cloud can yield substantial cost savings, potentially slashing IT operational expenses by as much as 50%. This reduction is achieved through lowered expenditures on resources, maintenance, and physical space.
Cloud migration enables companies to shift towards a model of operational expenditure. This transition means that businesses only spend money on the technology they actually use.
What are the common challenges faced during cloud migration?
Dealing with the hurdles of cloud migration frequently entails controlling expenses, securing data while adhering to compliance standards, bridging skill deficiencies, and confronting issues associated with legacy applications.
It is vital to proficiently tackle these obstacles in order to achieve a seamless shift to cloud computing.
How can organizations ensure data security during cloud migration?
To ensure data security during cloud migration, organizations must define compliance and security requirements in their migration plan, leverage automatic security updates and specialized tools from cloud providers, and adhere to relevant compliance laws like HIPAA and GDPR.
This proactive approach is essential for safeguarding sensitive information.
What factors should be considered when choosing a cloud provider?
It is critical to evaluate a cloud provider’s range of services, their system performance levels, the variety of pricing options they offer, available support channels, and their presence across different regions in light of your company’s specific requirements and strategic objectives.
A careful assessment that takes into account all these elements will help guarantee the selection of a cloud provider that most closely matches what your business seeks for its success.